Electrical Circuit elements:
Concept of ENERGY FLOW, with the help of this energy flow we will try to understand the property and behavior of electrical circuit elements.
When
energy flows from source to load, not 100% energy transferred to the load some
energy get lost during this process in the form of heat, many things happen to
the energy like transformed, unavailable and Stored.
1) Circuit Element Transformed: Energy transformed from
electrical to mechanical, electrical to magnetic and electrical to heat energy.
2) Circuit Element Unavailable: Some energy will get lost, it
means during the process of energy flow
it will become unavailable to the load, some amount of energy will dissipate as
heat.
3) Circuit Element Stored: During energy flow energy can be stored in two forms either in kinetic form or potential form, later can be recovered and send either to load or back to the source.So, the energy lost in the component is resistor(R), energy get stored in the kinetic form, component call as an Inductor (L) and in capacitor(C) energy is stored in the form of potential energy.
As we all
aware any electrical circuit mainly consists of these elements viz resistor, Inductor and capacitor. Property of these elements are resistance, inductance
and capacitance respectively.
We will see all the elements one by one to know them in more detail in below chapters.
RESISTOR
DEFINITION OF RESISTOR: Resistor is not a dynamic
component, it doesn't have history, memory and the past state.
It is the algebraic component, whatever is given to the input same will come as output.
✓ Property of Resistor:
•
Dissipative
• Lossy
- Characteristics of Resistor: Generally, we
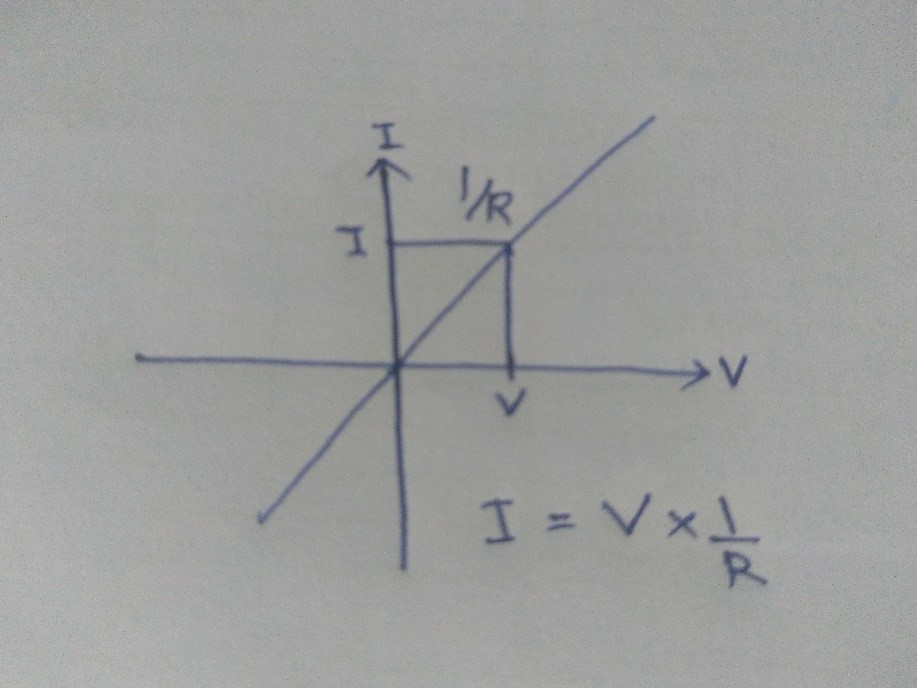
characterize the component in IV curve.
Fig.1 Characteristics of Resistor
Fig.2 Characteristics of Resistor
When
resistor line aligned with the current(I) axis then slop will be zero and R
will be infinite, which means it will represent short circuit at y axis. When
resistor line aligned with the voltage(V) axis then slop will be zero and R
will be infinite, which means it will represent open circuit at x axis. For
this refer fig.1.
With the
reference of fig.2
current (I)= Voltage (V)/Resistance (R) --------(1)
Or V=IR -------- Equation(2)
This is
known as ohm's law.
POWER DISSIPATION IN RESISTOR:
P=VI
Where,
V is the
voltage across the resistance.
I is the
current through the resistance.
According
to equation (2)
P=(V*I)*I
P=I²R
According
to equation (1)
P=V*(V/R)
P=V²/R
Resistance:
A material has property to oppose the flow of electrons through a given material, it is known as resistance of material. Different material has different resistivity like Aluminium, copper and gold has value of 2.82*10^-8 ohm-m, 1.72*10^-8 ohm-m and 2.44*10^-8 ohm-m respectively.
Thus,
resistance restricts the flow of electrons in the circuit.
What is the flow of electrons?
Flow of electrons is current, and current is nothing but the flow of electrons in the material/conduct.
As per the ohms law:
R=V/I
Where
R is
resistance of the circuit,which is considered as 1 ohm.
V is
voltage of the circuit, which is considered as 1 volt.
I is
current of the circuit, which is considered as 1 Ampere.
Note: When electric current flow
through the conductor it will generate heat due to collision of electrons
within atom.
HOW TO FIND THE VALUE OF RESISTOR?
Fig.3 Resistance Value
Fig.4 Resistance Value
Now we will see how to find the resistor value?
Consider
the above figure of resistor
Y
B R
4
6 2
This is
the resistor value = 46*10² ohms
Third
value is the multiplier.
Note: keep in mind the last colour
code of the resistor shows the tolerance, which means variation of resistance
with temperature.
RESISTOR SYMBOLS:
RESISTOR SYMBOL:
Fig. 5 Symbol of resistor
There are mainly two type of resistor available:
Fig (a):
Fixed resistor.
Fig (b):
Variable resistor.
Difference between fixed and variable resistor:
✓ Fixed resistor: This type of resistor value can't be varied once installed in the system.
✓ Variable resistor: Resistor value can be adjusted at any
time and any instant.
What is the Rheostat?
This is very useful to control the current of any circuit by varying the resistance.
To know more about resistor please visit the given link:
Elements of electrical circuit- Resistor
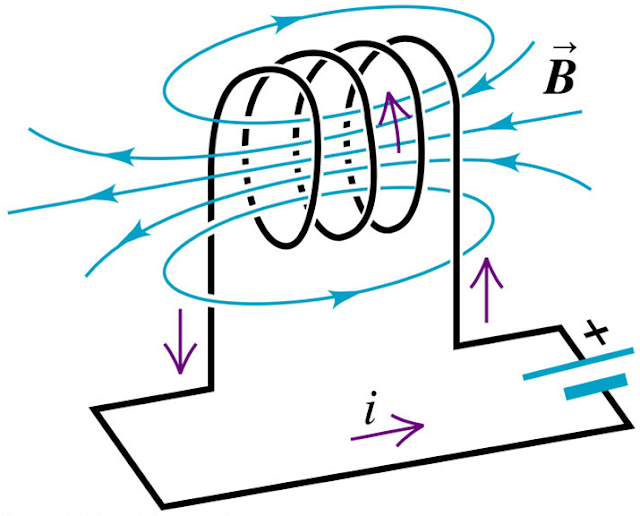
INDUCTANCE:
Fig.6 Inductor
Property of Inductor:
A
material has property to oppose any change of magnitude or direction of current
passing through the conductor, this property known as inductance. Its unit is
Henry(H).
In other
word we can say that, whenever current passes through a conductor, inductance
will oppose any change of magnitude and direction.
Inductance will be one Henry, when current through a coil of conductor changes at the rate of one ampere/second generating one volt across the coil.
Take one meter of conductor, twist it, it will become a simplest Inductor / coil.
As per
the ampere’s law when current will flow through a conductor, an electromagnetic
field will be formed around the conductor. However, if flow or direction of
current will change, the EMF changes.
Due to
this phenomenon voltage (V) will generate across the coil,
v =L di/dt
Where,
i is the current passing through an Inductor in Amp.
v is the
voltage across an Inductor or coil.
Voltage
across coil/Inductor will be zero if current through an Inductor remains
constant, there will not be inductance during steady state condition. It will
make coil/Inductor to behave as short circuit while switching across the d.c.
voltage and act as open circuit during steady state condition.
If
current magnitude or direction will change then inductance will appear in the
coil or Inductor.
Equation for power absorbed by Inductor:
P =Vi= Ldi/dt
. i
= Lidi/di watts
Energy storage equation:
E=1/2 Li
Joules
To know more about other Elements of electrical circuit please visit to below links.
CAPACITANCE
Definition of Capacitance:
Definition
of capacitance is, it’s a property of element to store/absorb electrical energy
within it. Capacitor is an energy storing element. A capacitor stores electric
energy in the form of potential energy in between two polarities of charges (i.e.
positive and negative charges) on the two electrodes of a capacitor. Measuring
unit of capacitance is farad.
Difference
between capacitor and resistor is, capacitor can store the energy whereas
resistor cannot store the energy.
Element in the circuit which has capacitance, namely known as capacitor.
Q stands
for amount of charge can be stored in a capacitor in the form of capacitance.
V stand for voltage against which the capacitance.
C = Q/V
or C = q/v
Q = CV
Where,
CV is equal to i*t [ Steady state equation Q = i * q]
i stand
for charging current of capacitor.
t stand
for time required to charge the capacitor.
Equation for capacitor to absorb/store power/energy is given by:
- Power absorption equation:
P = VI
= CV dV/dt
[ i = v dv/dt under dynamic condition ]
- Energy storage equation:
E = 1/2 CV2 Joules
Note: Capacitor has property to block dc power and allow ac to pass.
Why
capacitor blocks dc we will discuss in next session.
To know more about other Elements of electrical circuit please visit to below links.








Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the come box.